Difference between revisions of "Sun"
From The Flat Earth Wiki
PeteSvarrior (talk | contribs) |
PeteSvarrior (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
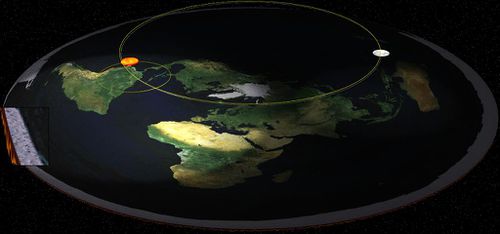
The '''sun''' is a rotating sphere. It has a diameter of 32 miles and is located approximately 3000 miles above the surface of the [[earth]]. | The '''sun''' is a rotating sphere. It has a diameter of 32 miles and is located approximately 3000 miles above the surface of the [[earth]]. | ||
| − | [[File:SarahSun2.gif|right]] | + | [[File:SarahSun2.gif|right|300px]] |
==Spotlight effect== | ==Spotlight effect== | ||
Revision as of 06:01, 1 June 2014
The sun is a rotating sphere. It has a diameter of 32 miles and is located approximately 3000 miles above the surface of the earth.
Spotlight effect
The Sun's area of light is limited to a circular area of light upon the earth much like the light of a lighthouse is limited to a finite circular area around it. The rotating light on a lighthouse does not propagate infinitely into the distance. This means that only certain portions of the Earth are lightened at a time. It also describes how night and day arise on a Flat Earth. The apparent view of rising and setting are caused by perspective, just as a flock of birds overhead will descend into the horizon as they fly into the distance.
Rendered picture of the Sun in relation to the Earth
More:
- Temperature Variations of sunlight
- Distance to the Sun
- The Seasons
- The Setting of the Sun
- Constant Speed of the Sun
- Magnification of the Sun at Sunset, or how the sun maintains its size throughout the day.