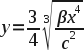Difference between revisions of "Electromagnetic Acceleration"
Tom Bishop (talk | contribs) |
Tom Bishop (talk | contribs) |
||
| (619 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
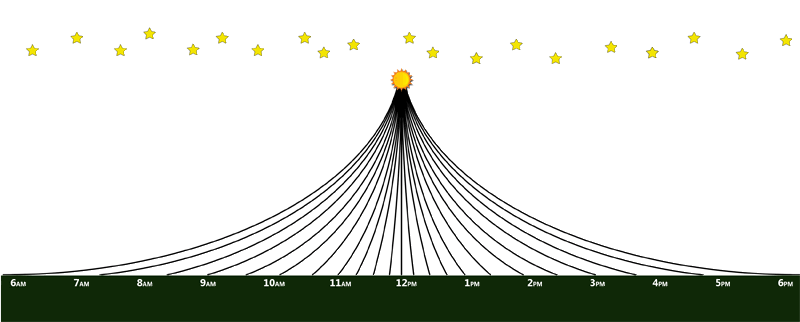
| − | The theory of the '''Electromagnetic Accelerator''' | + | The theory of the '''Electromagnetic Accelerator (EA)''' states that there is a mechanism to the universe that pulls, pushes, or deflects light upwards. All light curves upwards over very long distances. The Electromagnetic Accelerator has been adopted as a modern alternative to the perspective theory proposed in Earth Not a Globe. Sunrise and sunset happen as result of these upwardly curving light rays. |
[[File:Electromagnetic Accelerator.gif]] | [[File:Electromagnetic Accelerator.gif]] | ||
| − | The above illustration depicts rays from the | + | The above illustration depicts rays from the Sun which intersect with the earth. Other rays not depicted will miss the earth and make a curve back into space. |
| + | |||
| + | Electromagnetic Acceleration describes an intriguing equivalency. Astronomers of antiquity looked at light in the sky and assumed that light was straight to deduce a curved earth. When really, straight line trajectories do not generally occur in nature, and it was the light they were looking at that was curved. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The evidence given in favor of the upwards curving of light is prominent and extraordinary. It is given in the form of the '''[https://wiki.tfes.org/Electromagnetic_Acceleration#Evidence Celestial Sphere effects and Moon Tilt Illusion]''', in which straight line geometry does not apply to observations of the sky. Various large scale phenomena and features of the sky appear as if they were projected onto the concave surface of a planetarium dome above us, where straight lines become curves. The tails of comets, meteors, Aurora borialis, Milky Way, path of the Moon and Sun, and direction of the Moon's illuminated area, are all affected and warped upon the Celestial Sphere. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Theory= | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the astronomers of antiquity concluded from celestial observations that our Earth is a sphere, it stands that they may have had some reasoning to do so. The theory of Electromagnetic Acceleration provides the answer for ''why'' astronomers decided that our Earth was spherical, and also shows why this conclusion may have been a mistake. The error of classical astronomy is that its proponents did not bother to demonstrate the underlying assumptions. It was merely ''assumed,'' through human logic, that light would travel straightly at all distances and scales. Observation and interpretation was practiced to describe our world, but fallaciously, without empirical experimentation and verification of the fundamental axioms upon which those conclusions rely. | ||
| + | |||
| + | One may point out that it would be quite unreasonable to assert that a particle or wave in motion would travel forever through the universe in a perfectly straight line, unperturbed by any of the variety of forces or phenomena which fills existence. Get into a car and attempt to drive in a perfectly straight line down a highway without turning the steering wheel left or right. It is a near impossible thing to do. The car is affected by the slope and texture of the terrain, alignment of your wheels, the wind, &c. An apparently straight heading turns into a curved one. And when it comes to bullets, airplanes, et all, it is expected that bodies never realistically travel straightly. Straight line trajectories rarely, if ever, occur in nature. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Just why should we base anything in science on how we think a perfect world should be, without seeing actual demonstration that it is the case? It is most untenable to merely ''assume'' the workings of an unknown world. Often cited in the favor of Earth's rotundity are the rising and setting of celestial bodies, lunar phases, nearside face of the Moon always seen, dipping of the horizon, and red underlit clouds at sunset. Former Secretary of the Royal Astronomical Society, Augustus De Morgan, is noted to have defended the globular world of 1865 by asserting that "The evidence that the earth is round is but cumulative and circumstantial; scores of phenomena ask, separately and independently, what other explanation can be imagined except the sphericity of the Earth?"<sup>1</sup> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence we find an admission from astronomers of history that the spherical nature of the Earth was only ''imagined,'' in an effort to explain "scores of phenomena"; observational interpretation rather than controlled experimental probes of nature. Yet, in spite of such statements, it is seen that if light bends upwards over large scales then those same observations, which are typically cited to cumulate together as irrefutable evidence for rotundity, are readily explained. An assumption of Earth's rotundity is not required. Tweaking a single axiom can provide alternative explanation for the same phenomena. If two potential explanations can describe the same phenomena, the matter then becomes a philosophical question of what one might interpret as more reasonable. Should we assume that light is curving, or that the entire Earth is curving? Is it inconceivable that a bacterium at the center of a water droplet on a flat surface could also experience curving effects around it, and be the default for that situation? Would it be absurd to consider that we may be in a likewise situation with different affecting phenomena? Without positive evidence of the matter, an argument that there is no evidence that light is curving is consequently an admission that there is not sufficient evidence that light is straight. If it is not truly known how light behaves over ranges of hundreds and thousands of miles then one is merely pitting one hypothesis against another. | ||
| + | |||
| + | More significantly, the theory of Electromagnetic Acceleration does provide evidence. It not only explains what is cited for the Round Earth, but also appears to explain things which a Round Earth with straight line geometry does not explain. Celestial observations show that ''straight lines above us become curved'' <sup>2</sup>, as if our observations are projected onto the curved interior surface of a planetarium. The most striking example of such is the Moon Tilt Illusion<sup>3</sup>, where the path of light between the Sun and Moon seems to take a curved route, resulting in an illuminated portion of the Moon which points away from the Sun. The Milky Way, ecliptic of the Sun, tails of comets, meteors, and the aurora borialis also curve upon the 'celestial sphere'. An analysis of the celestial events above us shows that all which can be said to be in favor of a globe is actually a subset of the effect of Electromagnetic Acceleration, which gives the appearance of being inside of a dome. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Footnotes'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<sup>1</sup> Professor Augustus De Morgan, the ''Athenæum'' - March 25th, 1865, as cited in Chapter 1 of ''Earth Not a Globe''. Many similar modern expressions of this sentiment can be found today. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<sup>2</sup> See the '''[https://wiki.tfes.org/Electromagnetic_Acceleration#Evidence Evidence]''' section at the end of this article and the associated pages which cite observations of curving phenomena. Upwardly bending light causes straight lines in the sky to turn into concave downward curves to the observer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<sup>3</sup> The upward bending of light notably explains odd and extraordinary celestial anomalies such as the '''[[Moon Tilt Illusion]]''', in which the path of light between the Sun and Moon appears to take a curved path across the sky: | ||
| + | :[[File:Moon Tilt Diagram.png|550px]]<br> | ||
| + | ::<small>Image Credit: Professor Alan Myers ([https://web.archive.org/web/20190516183015/http://www.upenn.edu/emeritus/essays/MyersMoon.html Source])</small> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Approximation== | ||
| + | |||
| + | As there has been a long wait for a conclusive equation describing the Electromagnetic Acceleration theory, an approximate formula for large-scale bending has been authored and proposed by Parsifal. This is a limit of a more complex (and not yet final) expression as x approaches infinity, so this will only work when y is much greater than x - that is to say, when the vertical distance traveled is much greater than the horizontal distance traveled. Put another way, its accuracy will improve the closer the light ray is to vertical. Therefore, while it is not valid for short-range experiments, it can give an idea of how much sunlight would bend on its way to the Earth, for instance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Bendy.png]]<br> | ||
| + | <small>Credit: Parsifal</small> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where (0,0) is understood to be the point at which the light ray is horizontal (that is, the derivative of this function is zero). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Definition of terms: | ||
| + | |||
| + | x, y - co-ordinates in the plane of the light ray, where y is increasing in the direction of fastest decreasing Dark Energy potential, and x is increasing in the direction of the component of propagation of the ray which is perpendicular to y. | ||
| + | |||
| + | c - the speed of light in a vacuum. | ||
| + | |||
| + | β - the Bishop constant, which defines the magnitude of the acceleration on a horizontal light ray due to Dark Energy. When the theory is complete, attempts will be made to measure this experimentally. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is believed that the bending of light does not simulate the rate of globe earth curvature. Instead, the bending occurs more gradually over a greater distance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Articles of Interest== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[https://wtamu.edu/~cbaird/sq/2014/02/07/can-light-bend-around-corners/ Can light bend around corners?]''' ([https://web.archive.org/web/20200807221820/https://wtamu.edu/~cbaird/sq/2014/02/07/can-light-bend-around-corners/ Archive]) - West Texas A&M explains that the default assumption of straight line light trajectories is not true. Light's wave-like nature is very complex and bends on its own or along the surface of objects - "Yes, light can bend around corners. In fact, light ''always'' bends around corners to some extent." | ||
| + | *'''[https://physicsworld.com/a/light-bends-itself-round-corners/ Light Bends Itself Around Corners - Physicsworld.com]''' ([https://web.archive.org/web/20200117021226/https://physicsworld.com/a/light-bends-itself-round-corners/ Archive]) - A University of Central Florida research team demonstrated light beams which could self-accelerate, or bend, and were non-diffracting. | ||
| + | *'''[https://engineering.stanford.edu/magazine/article/taming-mavericks-stanford-researchers-use-synthetic-magnetism-control-light Stanford Researchers Use Synthetic Magnetism to Control Light]''' ([https://web.archive.org/web/20200117021228/https://engineering.stanford.edu/magazine/article/taming-mavericks-stanford-researchers-use-synthetic-magnetism-control-light Archive]) - Stanford researchers demonstrated a device that "produces a synthetic magnetism to exert virtual force on photons similar to the effect of magnets on electrons." | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Terrestrial= | ||
==Clouds Lit From Underside== | ==Clouds Lit From Underside== | ||
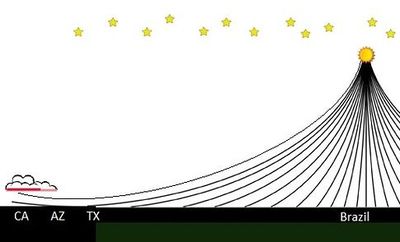
| − | Rays which miss the earth will turn back up into space, and may hit the underside of clouds before sunrise or after sunset. | + | Rays which miss the earth will turn back up into space, and may hit the underside of clouds before sunrise or after sunset, giving them a reddish glow. |
| − | [[File:EA-Clouds.jpg|400px]] | + | [[File:EA-Clouds.jpg|400px]]<br> |
| + | <small>Credit: Bobby Shafto</small> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Horizon Dip== | ||
| + | |||
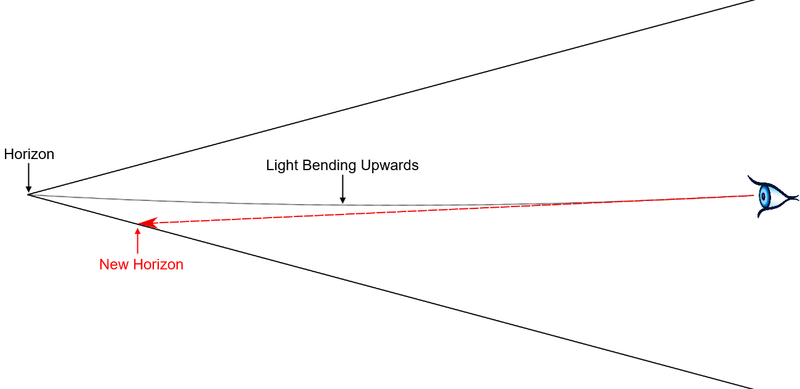
| + | The Electromagnetic Accelerator predicts that at high altitudes where one can see further into the distance, the horizon will dip below eye level. Light which travels parallel from the limits of vision will be pulled upwards and miss the eye of the observer. The rays the observer will see are those rays which are transmitted at a lower angle and pulled upwards to meet the observer, resulting in a horizon which is slightly below eye level. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:EA-Horizon.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since light in EA Theory is thought to curve more gradually than the claimed globe earth curvature, allowing one to see further into the distance that an RE should allow, the dip of the horizon at higher altitudes is seen to be higher than the globe earth prediction but lower than a planar prediction. See: '''[[High Altitude Horizon Dip]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Celestial= | ||
==Nearside Always Seen== | ==Nearside Always Seen== | ||
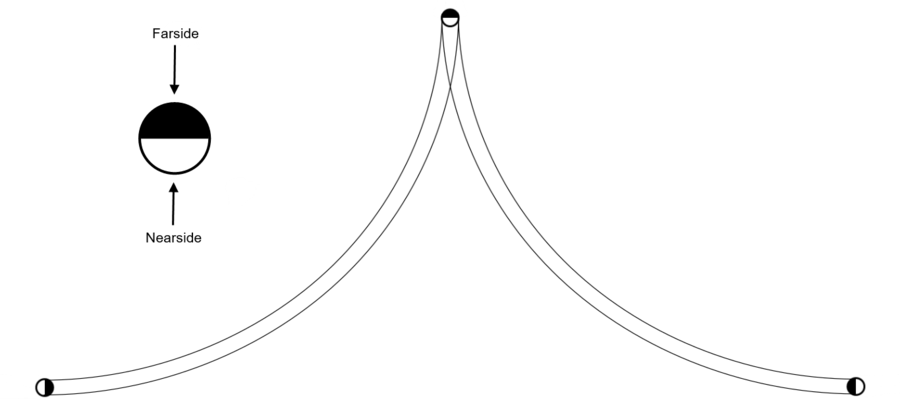
| − | A consequence of this paradigm is that the observer will always see the nearside (underside) of the celestial bodies. The below image depicts the extremes of the Moon's rising and setting. The image of the nearside face of the | + | A consequence of this paradigm of upwardly bending light is that the observer will always see the nearside (underside) of the celestial bodies. The below image depicts the extremes of the Moon's rising and setting. The image of the nearside face of the Moon is bent upwards around the Moon and faces the observers to either side of it. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Moon-face.png|900px]]<br> | ||
| + | <small>Concept: Pete Svarrior</small> | ||
| − | + | Essentially the light from the moon cascades straight down and arcs as it approaches the earth, so that at any viewpoint, we see the face of the moon that is facing straight down. This scheme also predicts that the image of the Moon will be flipped upside-down between rising and setting, or as seen in the North and South. | |
==Lunar Phases== | ==Lunar Phases== | ||
| − | + | When one observes the phases of the Moon they are seeing the Moon's day and night, a shadow created from the Sun illuminating half of the spherical Moon at any one time. As depicted in the previous section, due to EA we are always observing the nearside (or underside) of the Moon. | |
| + | |||
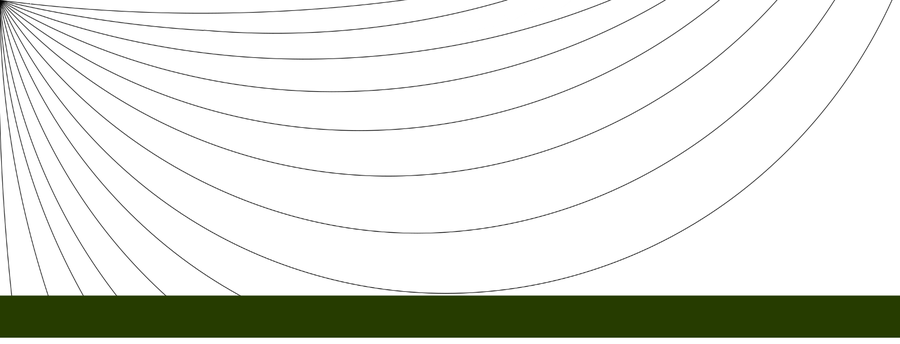
| + | The curved rays of the Sun results in the phases upon the Moon's surface. The plane of the Moon's route is at an inclination to the plane of the Sun's ecliptic, with its highest side opposite from the Sun. When the Moon is far from the Sun and higher than it, the Full Moon occurs. When the Moon is closer to the Sun and lower than it, the New Moon occurs<sup>1</sup>. The Moon moves in the same direction as the Sun at a slightly slower rate across the sky, lagging about 50 minutes behind daily, causing the range of phases. The time between two Full Moons, or between successive occurrences of the same phase, is about 29.53 days (29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes) on average. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sample large-scale Sun ray diagram (side view): | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:EA-Rays-2.png|900px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Lunar-Phases-Nodes.png|900px|link=https://wiki.tfes.org/images/c/c2/Lunar-Phases-Nodes.png]]<br> | ||
| + | <small>Concept: Curious Squirrel, totallackey</small> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Moon Position Table=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compare the above with the following table [http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/about-us/46-our-solar-system/the-moon/observing-the-moon/128-how-does-the-position-of-moonrise-and-moonset-change-intermediate from Cornell University] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20190506054437/http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/about-us/46-our-solar-system/the-moon/observing-the-moon/128-how-does-the-position-of-moonrise-and-moonset-change-intermediate Archive]), which provides a rule-of-thumb summation for when the Moon rises and sets during its phases: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! style="font-weight:bold;" | Moon phase | ||
| + | ! style="font-weight:bold;" | Moonrise | ||
| + | ! style="font-weight:bold;" | Moonset | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | New | ||
| + | | Sunrise | ||
| + | | Sunset | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1st quarter | ||
| + | | Local noon | ||
| + | | Local midnight | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Full | ||
| + | | Sunset | ||
| + | | Sunrise | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3rd quarter | ||
| + | | Local midnight | ||
| + | | Local noon | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ''Footnote'' | |
| − | + | <sup>1</sup> Around the time of the New Moon the Moon is not technically seen. According to [https://www.kean.edu/~fosborne/resources/ex11b2.htm Kean University] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20190529173255/https://www.kean.edu/~fosborne/resources/ex11b2.htm Archive]): {{cite|The New Moon begins the lunar cycle. The age of the Moon in a lunar cycle is measured from the time of New Moon. At New Moon the Earth, Moon and Sun are lined up. Because of the glare of the Sun, the Moon cannot be seen for a few days. After about 3 days, it is possible to see a thin crescent in the West or Southwest at sunset.}} | |
| − | + | ==Lunar Eclipse== | |
| − | + | The Lunar Eclipse may occur on an occasion when the Full Moon temporarily moves beyond the vertical rays of the Sun, causing a darkened area to manifest upon its surface. | |
| − | + | See: '''[[Lunar Eclipse due to Electromagnetic Acceleration]]''' | |
| − | [[File:EA- | + | =Evidence= |
| + | |||
| + | The apparent equivalency to the phenomena cited for the Round Earth Theory is not a coincidence. The EA Theory makes the same predictions, including ones not predicted by a Round Earth with straight line geometry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Celestial Sphere== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Electromagnetic Acceleration predicts that our observations of the sky would appear as if they were projected onto the inside surface of a dome. And indeed, this is what we experience. Straight line geometry stops working in the distance. When looking out over large distances it appears as if we are on the inside of a planetarium where ''straight lines become curved on a dome surface.'' Astronomers acknowledge this effect and attribute the phenomena to the Celestial Sphere, which posits that our celestial observations act as if they are projected onto a sphere around the observer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Projected onto a Dome=== | ||
| + | |||
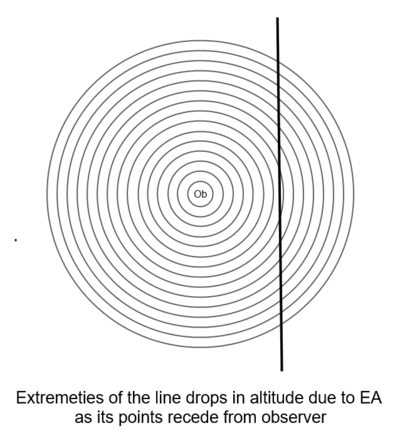
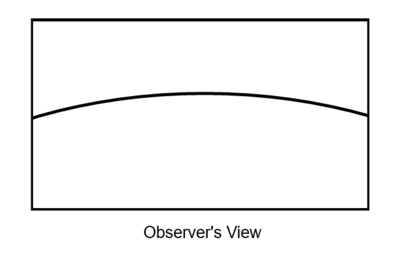
| + | As points in space recede from the observer they will lower in altitude due to the effect of Electromagnetic Acceleration, like how the Sun lowers as it recedes from the observer, causing celestial lines in space to generally appear as if they are being projected onto a curved surface. As an example, consider a straight line suspended high over and in front of an observer. From the observer's vantage point the points receding from the center of the line will appear to dip towards the ground due to EA, since those points are becoming more distant in relation to the observer. The straight line will appear curved on a 'celestial dome'. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:EA Drop1.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:EA-Curved.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This effect applies to celestial phenomena of sufficient length or duration. The tails of comets, meteors, Aurora borialis, Milky Way, path of the Moon and Sun, and direction of the Moon's illuminated area, are all affected and warped upon the Celestial Sphere. See the '''[[Celestial Sphere]]''' page for citations regarding astronomical phenomena. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Moon Tilt Illusion== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Electromagnetic Accelerator is able to make unique predictions. If the Sun is illuminating the Moon under straight line geometry, such as in RET, then it would be expected that the illuminated portion of the Moon will always point at the Sun, much like how when shining a flashlight at a ball the illuminated portion of the ball will always appear to point at the flashlight to observers positioned around the ball. It is natural and expected that the illuminated portion of a body will appear to point at its light source, like an arrow will point at its destination in space. Because straight line paths are warped into curves due to Electromagnetic Acceleration, however, the light from the Sun will be seen take an apparently curved path, causing the illuminated portion of the Moon to point ''away'' from the Sun. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Moon Tilt Diagram.png|600px]]<br> | ||
| + | <small>Credit: Professor Alan Myers ([https://web.archive.org/web/20190516183015/http://www.upenn.edu/emeritus/essays/MyersMoon.html Source])</small> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See the '''[[Moon Tilt Illusion]]''' page for a list of observations and diagrams. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Topics== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Sunrise and Sunset]]''' - Sunrise and Sunset Main Page | ||
| + | |||
| + | :*'''[[Electromagnetic Acceleration]]''' - EA Main Page | ||
| + | ::*'''[[Lunar Eclipse due to Electromagnetic Acceleration]]''' - The Lunar Eclipse occurs when the Moon moves beyond the Sun's light | ||
| + | ::*'''[[Celestial Sphere]]''' - The tails of comets, Aurora Borealis, Milky Way, and the path of the Moon and Sun are warped on a 'Celestial Sphere' | ||
| + | ::*'''[[Moon Tilt Illusion]]''' - Illuminated portion of the Moon does not point in the expected direction | ||
| + | ::*'''[[High Altitude Horizon Dip]]''' - Horizon dip at high altitudes may suggest a bending of light | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Cosmos]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Sun]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Moon]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Electromagnetic Acceleration]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:42, 24 March 2023
The theory of the Electromagnetic Accelerator (EA) states that there is a mechanism to the universe that pulls, pushes, or deflects light upwards. All light curves upwards over very long distances. The Electromagnetic Accelerator has been adopted as a modern alternative to the perspective theory proposed in Earth Not a Globe. Sunrise and sunset happen as result of these upwardly curving light rays.
The above illustration depicts rays from the Sun which intersect with the earth. Other rays not depicted will miss the earth and make a curve back into space.
Electromagnetic Acceleration describes an intriguing equivalency. Astronomers of antiquity looked at light in the sky and assumed that light was straight to deduce a curved earth. When really, straight line trajectories do not generally occur in nature, and it was the light they were looking at that was curved.
The evidence given in favor of the upwards curving of light is prominent and extraordinary. It is given in the form of the Celestial Sphere effects and Moon Tilt Illusion, in which straight line geometry does not apply to observations of the sky. Various large scale phenomena and features of the sky appear as if they were projected onto the concave surface of a planetarium dome above us, where straight lines become curves. The tails of comets, meteors, Aurora borialis, Milky Way, path of the Moon and Sun, and direction of the Moon's illuminated area, are all affected and warped upon the Celestial Sphere.
Theory
If the astronomers of antiquity concluded from celestial observations that our Earth is a sphere, it stands that they may have had some reasoning to do so. The theory of Electromagnetic Acceleration provides the answer for why astronomers decided that our Earth was spherical, and also shows why this conclusion may have been a mistake. The error of classical astronomy is that its proponents did not bother to demonstrate the underlying assumptions. It was merely assumed, through human logic, that light would travel straightly at all distances and scales. Observation and interpretation was practiced to describe our world, but fallaciously, without empirical experimentation and verification of the fundamental axioms upon which those conclusions rely.
One may point out that it would be quite unreasonable to assert that a particle or wave in motion would travel forever through the universe in a perfectly straight line, unperturbed by any of the variety of forces or phenomena which fills existence. Get into a car and attempt to drive in a perfectly straight line down a highway without turning the steering wheel left or right. It is a near impossible thing to do. The car is affected by the slope and texture of the terrain, alignment of your wheels, the wind, &c. An apparently straight heading turns into a curved one. And when it comes to bullets, airplanes, et all, it is expected that bodies never realistically travel straightly. Straight line trajectories rarely, if ever, occur in nature.
Just why should we base anything in science on how we think a perfect world should be, without seeing actual demonstration that it is the case? It is most untenable to merely assume the workings of an unknown world. Often cited in the favor of Earth's rotundity are the rising and setting of celestial bodies, lunar phases, nearside face of the Moon always seen, dipping of the horizon, and red underlit clouds at sunset. Former Secretary of the Royal Astronomical Society, Augustus De Morgan, is noted to have defended the globular world of 1865 by asserting that "The evidence that the earth is round is but cumulative and circumstantial; scores of phenomena ask, separately and independently, what other explanation can be imagined except the sphericity of the Earth?"1
Hence we find an admission from astronomers of history that the spherical nature of the Earth was only imagined, in an effort to explain "scores of phenomena"; observational interpretation rather than controlled experimental probes of nature. Yet, in spite of such statements, it is seen that if light bends upwards over large scales then those same observations, which are typically cited to cumulate together as irrefutable evidence for rotundity, are readily explained. An assumption of Earth's rotundity is not required. Tweaking a single axiom can provide alternative explanation for the same phenomena. If two potential explanations can describe the same phenomena, the matter then becomes a philosophical question of what one might interpret as more reasonable. Should we assume that light is curving, or that the entire Earth is curving? Is it inconceivable that a bacterium at the center of a water droplet on a flat surface could also experience curving effects around it, and be the default for that situation? Would it be absurd to consider that we may be in a likewise situation with different affecting phenomena? Without positive evidence of the matter, an argument that there is no evidence that light is curving is consequently an admission that there is not sufficient evidence that light is straight. If it is not truly known how light behaves over ranges of hundreds and thousands of miles then one is merely pitting one hypothesis against another.
More significantly, the theory of Electromagnetic Acceleration does provide evidence. It not only explains what is cited for the Round Earth, but also appears to explain things which a Round Earth with straight line geometry does not explain. Celestial observations show that straight lines above us become curved 2, as if our observations are projected onto the curved interior surface of a planetarium. The most striking example of such is the Moon Tilt Illusion3, where the path of light between the Sun and Moon seems to take a curved route, resulting in an illuminated portion of the Moon which points away from the Sun. The Milky Way, ecliptic of the Sun, tails of comets, meteors, and the aurora borialis also curve upon the 'celestial sphere'. An analysis of the celestial events above us shows that all which can be said to be in favor of a globe is actually a subset of the effect of Electromagnetic Acceleration, which gives the appearance of being inside of a dome.
Footnotes
- 1 Professor Augustus De Morgan, the Athenæum - March 25th, 1865, as cited in Chapter 1 of Earth Not a Globe. Many similar modern expressions of this sentiment can be found today.
- 2 See the Evidence section at the end of this article and the associated pages which cite observations of curving phenomena. Upwardly bending light causes straight lines in the sky to turn into concave downward curves to the observer.
- 3 The upward bending of light notably explains odd and extraordinary celestial anomalies such as the Moon Tilt Illusion, in which the path of light between the Sun and Moon appears to take a curved path across the sky:
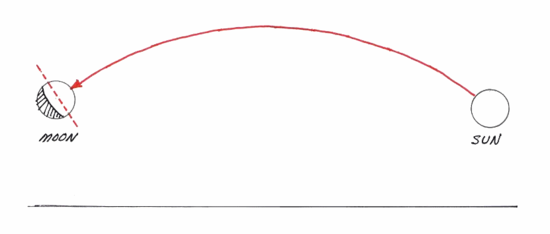
- Image Credit: Professor Alan Myers (Source)
Approximation
As there has been a long wait for a conclusive equation describing the Electromagnetic Acceleration theory, an approximate formula for large-scale bending has been authored and proposed by Parsifal. This is a limit of a more complex (and not yet final) expression as x approaches infinity, so this will only work when y is much greater than x - that is to say, when the vertical distance traveled is much greater than the horizontal distance traveled. Put another way, its accuracy will improve the closer the light ray is to vertical. Therefore, while it is not valid for short-range experiments, it can give an idea of how much sunlight would bend on its way to the Earth, for instance.
Where (0,0) is understood to be the point at which the light ray is horizontal (that is, the derivative of this function is zero).
Definition of terms:
x, y - co-ordinates in the plane of the light ray, where y is increasing in the direction of fastest decreasing Dark Energy potential, and x is increasing in the direction of the component of propagation of the ray which is perpendicular to y.
c - the speed of light in a vacuum.
β - the Bishop constant, which defines the magnitude of the acceleration on a horizontal light ray due to Dark Energy. When the theory is complete, attempts will be made to measure this experimentally.
It is believed that the bending of light does not simulate the rate of globe earth curvature. Instead, the bending occurs more gradually over a greater distance.
Articles of Interest
- Can light bend around corners? (Archive) - West Texas A&M explains that the default assumption of straight line light trajectories is not true. Light's wave-like nature is very complex and bends on its own or along the surface of objects - "Yes, light can bend around corners. In fact, light always bends around corners to some extent."
- Light Bends Itself Around Corners - Physicsworld.com (Archive) - A University of Central Florida research team demonstrated light beams which could self-accelerate, or bend, and were non-diffracting.
- Stanford Researchers Use Synthetic Magnetism to Control Light (Archive) - Stanford researchers demonstrated a device that "produces a synthetic magnetism to exert virtual force on photons similar to the effect of magnets on electrons."
Terrestrial
Clouds Lit From Underside
Rays which miss the earth will turn back up into space, and may hit the underside of clouds before sunrise or after sunset, giving them a reddish glow.
Horizon Dip
The Electromagnetic Accelerator predicts that at high altitudes where one can see further into the distance, the horizon will dip below eye level. Light which travels parallel from the limits of vision will be pulled upwards and miss the eye of the observer. The rays the observer will see are those rays which are transmitted at a lower angle and pulled upwards to meet the observer, resulting in a horizon which is slightly below eye level.
Since light in EA Theory is thought to curve more gradually than the claimed globe earth curvature, allowing one to see further into the distance that an RE should allow, the dip of the horizon at higher altitudes is seen to be higher than the globe earth prediction but lower than a planar prediction. See: High Altitude Horizon Dip
Celestial
Nearside Always Seen
A consequence of this paradigm of upwardly bending light is that the observer will always see the nearside (underside) of the celestial bodies. The below image depicts the extremes of the Moon's rising and setting. The image of the nearside face of the Moon is bent upwards around the Moon and faces the observers to either side of it.
Essentially the light from the moon cascades straight down and arcs as it approaches the earth, so that at any viewpoint, we see the face of the moon that is facing straight down. This scheme also predicts that the image of the Moon will be flipped upside-down between rising and setting, or as seen in the North and South.
Lunar Phases
When one observes the phases of the Moon they are seeing the Moon's day and night, a shadow created from the Sun illuminating half of the spherical Moon at any one time. As depicted in the previous section, due to EA we are always observing the nearside (or underside) of the Moon.
The curved rays of the Sun results in the phases upon the Moon's surface. The plane of the Moon's route is at an inclination to the plane of the Sun's ecliptic, with its highest side opposite from the Sun. When the Moon is far from the Sun and higher than it, the Full Moon occurs. When the Moon is closer to the Sun and lower than it, the New Moon occurs1. The Moon moves in the same direction as the Sun at a slightly slower rate across the sky, lagging about 50 minutes behind daily, causing the range of phases. The time between two Full Moons, or between successive occurrences of the same phase, is about 29.53 days (29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes) on average.
Sample large-scale Sun ray diagram (side view):
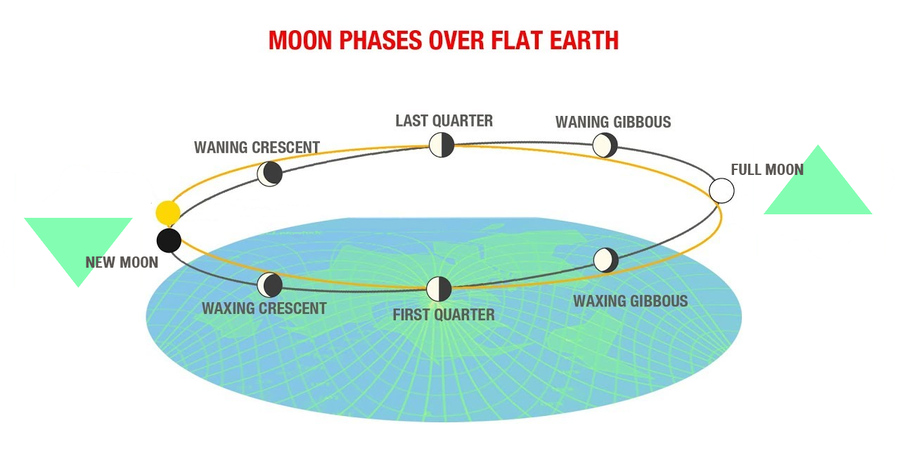
Concept: Curious Squirrel, totallackey
Moon Position Table
Compare the above with the following table from Cornell University (Archive), which provides a rule-of-thumb summation for when the Moon rises and sets during its phases:
| Moon phase | Moonrise | Moonset |
|---|---|---|
| New | Sunrise | Sunset |
| 1st quarter | Local noon | Local midnight |
| Full | Sunset | Sunrise |
| 3rd quarter | Local midnight | Local noon |
Footnote
1 Around the time of the New Moon the Moon is not technically seen. According to Kean University (Archive): “ The New Moon begins the lunar cycle. The age of the Moon in a lunar cycle is measured from the time of New Moon. At New Moon the Earth, Moon and Sun are lined up. Because of the glare of the Sun, the Moon cannot be seen for a few days. After about 3 days, it is possible to see a thin crescent in the West or Southwest at sunset. ”
Lunar Eclipse
The Lunar Eclipse may occur on an occasion when the Full Moon temporarily moves beyond the vertical rays of the Sun, causing a darkened area to manifest upon its surface.
See: Lunar Eclipse due to Electromagnetic Acceleration
Evidence
The apparent equivalency to the phenomena cited for the Round Earth Theory is not a coincidence. The EA Theory makes the same predictions, including ones not predicted by a Round Earth with straight line geometry.
Celestial Sphere
Electromagnetic Acceleration predicts that our observations of the sky would appear as if they were projected onto the inside surface of a dome. And indeed, this is what we experience. Straight line geometry stops working in the distance. When looking out over large distances it appears as if we are on the inside of a planetarium where straight lines become curved on a dome surface. Astronomers acknowledge this effect and attribute the phenomena to the Celestial Sphere, which posits that our celestial observations act as if they are projected onto a sphere around the observer.
Projected onto a Dome
As points in space recede from the observer they will lower in altitude due to the effect of Electromagnetic Acceleration, like how the Sun lowers as it recedes from the observer, causing celestial lines in space to generally appear as if they are being projected onto a curved surface. As an example, consider a straight line suspended high over and in front of an observer. From the observer's vantage point the points receding from the center of the line will appear to dip towards the ground due to EA, since those points are becoming more distant in relation to the observer. The straight line will appear curved on a 'celestial dome'.
This effect applies to celestial phenomena of sufficient length or duration. The tails of comets, meteors, Aurora borialis, Milky Way, path of the Moon and Sun, and direction of the Moon's illuminated area, are all affected and warped upon the Celestial Sphere. See the Celestial Sphere page for citations regarding astronomical phenomena.
Moon Tilt Illusion
The Electromagnetic Accelerator is able to make unique predictions. If the Sun is illuminating the Moon under straight line geometry, such as in RET, then it would be expected that the illuminated portion of the Moon will always point at the Sun, much like how when shining a flashlight at a ball the illuminated portion of the ball will always appear to point at the flashlight to observers positioned around the ball. It is natural and expected that the illuminated portion of a body will appear to point at its light source, like an arrow will point at its destination in space. Because straight line paths are warped into curves due to Electromagnetic Acceleration, however, the light from the Sun will be seen take an apparently curved path, causing the illuminated portion of the Moon to point away from the Sun.
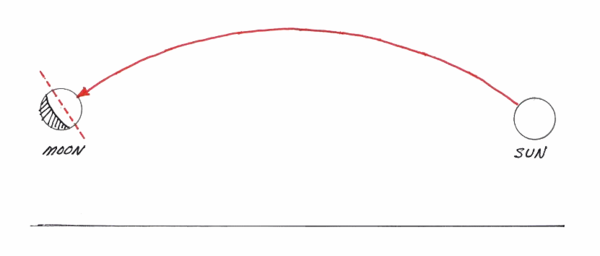
Credit: Professor Alan Myers (Source)
See the Moon Tilt Illusion page for a list of observations and diagrams.
Topics
Sunrise and Sunset - Sunrise and Sunset Main Page
- Electromagnetic Acceleration - EA Main Page
- Lunar Eclipse due to Electromagnetic Acceleration - The Lunar Eclipse occurs when the Moon moves beyond the Sun's light
- Celestial Sphere - The tails of comets, Aurora Borealis, Milky Way, and the path of the Moon and Sun are warped on a 'Celestial Sphere'
- Moon Tilt Illusion - Illuminated portion of the Moon does not point in the expected direction
- High Altitude Horizon Dip - Horizon dip at high altitudes may suggest a bending of light