Difference between revisions of "Ring Laser Gyroscope"
Tom Bishop (talk | contribs) |
Tom Bishop (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
:*[https://www.europhysicsnews.org/articles/epn/pdf/2017/04/epn2017484p25.pdf Ring Lasers - a brief history] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20190611180957/https://www.europhysicsnews.org/articles/epn/pdf/2017/04/epn2017484p25.pdf Archive]) - Describes that the Ring Laser Gyroscope is a Sagnac/MGP device. | :*[https://www.europhysicsnews.org/articles/epn/pdf/2017/04/epn2017484p25.pdf Ring Lasers - a brief history] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20190611180957/https://www.europhysicsnews.org/articles/epn/pdf/2017/04/epn2017484p25.pdf Archive]) - Describes that the Ring Laser Gyroscope is a Sagnac/MGP device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Raw Data= | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==MEMS Gyroscope== | ||
| + | |||
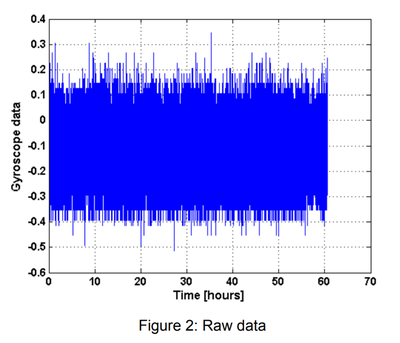
| + | Raw data from Section 4.1 of a paper titled [http://www.tkt.cs.tut.fi/research/nappo_files/Symposium_Gyro_Technology_2010_web.pdf Measuring the Earth’s Rotation Rate Using a Low-Cost MEMS Gyroscope ([https://web.archive.org/web/20191024195012/http://www.tkt.cs.tut.fi/research/nappo_files/Symposium_Gyro_Technology_2010_web.pdf Archive] shows that the raw data is inconsistent and noisy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{cite|During the measurements the gyroscope was stationary on the floor. Its positive sensitive axis was parallel to the local horizontal plane. Total data collection time of the experiment spans to approximately 61 hours. The raw data collected directly from the sensor is shown in Figure 2 as a function of time.}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:MEMS Gyro Raw.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
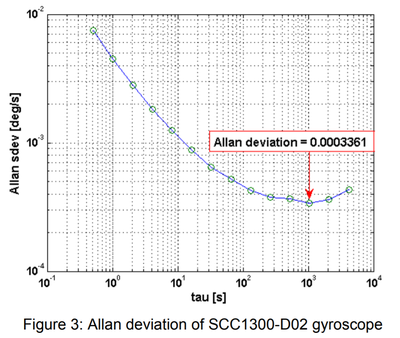
| + | With noise analysis the earth's rotation is interpreted and pulled out with an algorithm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:MEMS Gyro Allan Deviation.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{cite|From the Allan variance plot it can be seen that bias instability is approximately | ||
| + | 0.00034 deg s which equals about 1.2 deg h . The result agrees well with the | ||
| + | specifications, taking into account the temperature fluctuations during the measurements. | ||
| + | In conclusion, the noise level of the new SCC1300-D02 gyroscope is low enough to | ||
| + | theoretically measure the angular velocity of the Earth.}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | We see that it is through the interpretation of noise can the rotation of the earth be found. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Revision as of 20:01, 24 October 2019
The Ring Laser Gyroscope is a consumer device version of the Michelson-Gale-Pearson Experiment. The principle of operation of these devices is based on the Sagnac Effect, which was famed for showing that light changes velocity on a rotating platform. In the RLG and MGP experiment the Earth is used as the 'rotating platform'. Like with the Michelson-Gale-Pearson Experiment, some have alleged that Ring Laser Gyroscopes have detected the rotation of the earth.
From a work titled The Sagnac and Michelson-Gale-Pearson Experiments (Archive) by Dr. Paulo N. Correa we read on p.5:
“ The outcome of the MGP experiment was ambiguous, though maybe no more ambiguous than the small persistent positive shift observed in MM experiments. Composed of 269 separate tests with readings that varied from -0.04 to +0.55 of a fringe, and a mean at +0.26 fringes, the MGP experiment could be interpreted to yield a positive result of ≈ 0.3 km/s - therefore near the speed of the earth's rotation, but the result was of borderline significance. It could be said that the experiment was inconclusive because it adduced neither proof that there was a shift in the phase of the light beams, nor that there wasn't one. ”
Essentially the tests saw wild results. There was almost no change to light's velocity in one test, and then a lot of change in another test. It is perplexing that the rotation of the earth would start and stop when tested at different times. Only through the statistics was it claimed that the experiment saw the rotation of the earth. The inconsistent results were ambiguous in nature and could offer no evidence of the shift in the phase of the light beams.
As stated above, the results of the Michelson-Gale-Pearson experiment were inconsistent and an algorithm was applied to get the desired result. If we are to say that the Ring Laser Gyroscope is the same device, then the same criticism would apply.
Cause of Noise
While inconsistent experiments are invalid as demonstration of any particular cause, one potential cause of the noise in these very sensitive devices is seismic disturbance. See: Ring Laser Gyroscope - Seismology
Ring Interferometer
Micheson-Gale was a ring interferometer and the basis for all ring interferometers to come after this experiment. Its Wikipedia article says:
“ The Michelson-Gale experiment was a very large ring interferometer, (a perimeter of 1.9 kilometer) ”
The second slide in a presentation titled "Ring Laser Gyroscope Measurement of Absolute Earth Rotation" introduces the Michelson-Gale experiment as basis for the Ring Laser Gyroscope:
Ring Laser Gyroscope Measurement of Absolute Earth Rotation
3rd International Workshop on Rotational Seismology
https://slideplayer.com/slide/10532529/
Further Reference
- Ring Lasers - a brief history (Archive) - Describes that the Ring Laser Gyroscope is a Sagnac/MGP device.
Raw Data
MEMS Gyroscope
Raw data from Section 4.1 of a paper titled Measuring the Earth’s Rotation Rate Using a Low-Cost MEMS Gyroscope ([https://web.archive.org/web/20191024195012/http://www.tkt.cs.tut.fi/research/nappo_files/Symposium_Gyro_Technology_2010_web.pdf Archive shows that the raw data is inconsistent and noisy.
“ During the measurements the gyroscope was stationary on the floor. Its positive sensitive axis was parallel to the local horizontal plane. Total data collection time of the experiment spans to approximately 61 hours. The raw data collected directly from the sensor is shown in Figure 2 as a function of time. ”
With noise analysis the earth's rotation is interpreted and pulled out with an algorithm.
“ From the Allan variance plot it can be seen that bias instability is approximately 0.00034 deg s which equals about 1.2 deg h . The result agrees well with the specifications, taking into account the temperature fluctuations during the measurements. In conclusion, the noise level of the new SCC1300-D02 gyroscope is low enough to theoretically measure the angular velocity of the Earth. ”
We see that it is through the interpretation of noise can the rotation of the earth be found.