Sun
From The Flat Earth Wiki
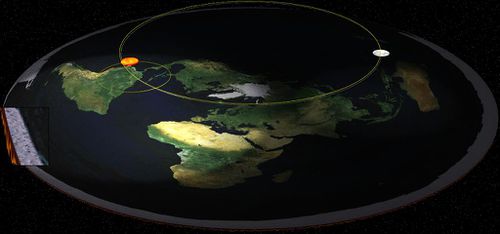
The Sun is a revolving sphere. It has a diameter of 32 miles and is located approximately 3000 miles above the surface of the Earth.
Topics
- Sunrise and Sunset - Sunrise and Sunset Main Page
- Electromagnetic Acceleration describes the rising and setting of the Sun, as well as several other phenomena
- The Setting of the Sun as a Perspective Effect describes the traditional interpretation of sunsets as originally described by Samuel Rowbotham
- Magnification of the Sun at Sunset describes why the Sun does not shrink as it recedes
- The Equinox page describes why the Sun rises and sets from a generally Eastward and Westward direction
- Temperature Variations of sunlight
- Distance to the Sun
- The Seasons
- Clouds Lit From Below
Spotlight effect
The Sun's area of light is limited to an elliptic area of light upon the earth much like the light of a lighthouse is limited to a finite area around it. The rotating light on a lighthouse does not propagate infinitely into the distance. This means that only certain portions of the Earth are lightened at a time. It also describes how night and day arise on a Flat Earth. The apparent view of rising and setting are caused by perspective, just as a flock of birds overhead will descend into the horizon as they fly into the distance.